Article
The Impact of Data Science on Branding


In June 2010, Mike Loukides, Vice President of Content Strategy for O'Reilly Media Inc., penned an influential piece titled What is Data Science? He noted:
"The question facing every company today, every startup, every non-profit, every project site that wants to attract a community, is how to use data effectively — not just their own data, but all the data that’s available and relevant.”
Words with weight when you consider the abundance of information at our fingertips. Harnessing it to drive meaningful change is a challenge with no hard-and-fast solution.
Every data set tells a story, which is vital for brands to uncover and articulate. Data presents a unique opportunity to connect the dots, be intentional in your decisions and inspire belief among your stakeholders.
But the way to use data depends on many different factors – not least of which is the type of organization and its circumstances.
With that in mind, let’s explore how companies can create and sustain customer value using a distinct data science framework. It’s called Customer-Based-Execution and Strategy (CUBES), which:
- Outlines the components of customer value
- Examines the link to business outcomes
- Explains how you can build, retain and improve that value
The CUBES framework enables your executives to interpret the complex connections between the drivers (inputs), components (throughputs) and business outcomes (outputs) of customer value. These connections change over time, and they vary based on the types of businesses you serve.
Inputs, throughputs and Outputs
You can associate inputs to operational investments that affect your buyers’ perceptions. From staff and technology to infrastructure and brand equity. They all have a role in creating value when customers use your product or service.
Throughputs, on the other hand, are your buyers’ perceptions of these inputs and your brand. And outputs are defined by the relationship between overall customer value and your business outcomes – whether they’re loyalty behaviors or financial results.
There are also several external aspects you can add to the CUBES framework, including:
- Policies and regulations
- Economic conditions
- Culture and competition
- Technical developments
Say your company is a computer chip manufacturer. You would probably need to hire highly-skilled engineers who can design and build quality chips. As a result, your ability to provide value to customers will depend on labor market conditions and competition with other manufacturers.
It all ties back to your brand’s ability to resonate with your target audience, so you can carve a distinct position, outperform and outlast your competitors.
A Closer Look at the CUBES Framework
More examples are emerging that validate the link between key customer behaviors and business outcomes. For instance, we’ve seen how retention and word of mouth improve business outcomes like sales, margins and stock value.
Which is where the CUBES framework comes in handy. Using customer satisfaction as a barometer of customer value, you can associate the impact of operational investments to customer loyalty, sales
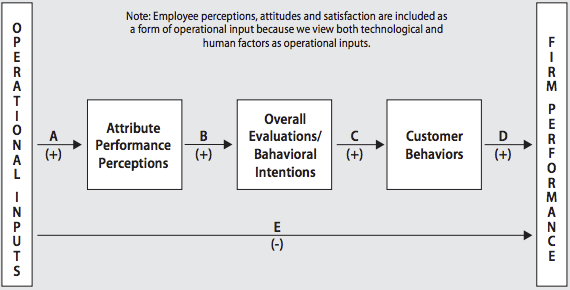
The Customer-Based Execution & Strategy Framework, courtesy of C-CUBES™
The CUBES framework enables you to enhance customer value through two distinct models.
Strategic Model
The strategic CUBES model identifies the operational inputs that affect your buyers’ perceptions of attribute performance. Let’s dial back for a moment to the scenario where you’re a computer chip manufacturer.
An example of attribute perception would be how your customers evaluate your support technicians’ responsiveness to their inquiries. Whereas an operational input to attribute perception would be your decision to increase the number of support technicians to improve responsiveness.
Using the strategic model, you can determine how the increased number of support technicians affects your buyers’ perceptions of their responsiveness. This type of insight helps inform important business decisions, such as where to invest resources so they truly count.
Operational Model
The operational model focuses on implementation, with the goal of increasing efficiency, providing usable key performance indicators (KPIs) and accomplishing certain benchmarks.
These KPIs can be established at the customer and business unit levels. Depending on the data that’s available, it could be geographic areas and decision-making departments, respectively.
By evaluating these KPIs, you can develop short- and medium-term metrics to make sure the strategic model is followed throughout your company.
In the chip manufacturer scenario, the operational model allows you to compare business units based on metrics that measure the responsiveness of your support technicians. Such as response time, service turnaround time and percentage of calls returned within, say, two hours.
You can also compare the business units from a customer satisfaction perspective. Not only to identify which drivers are more important to your target audience but also to segment buyers based on the differences within these drivers. As a result, you can then create specific dashboards and incentive programs.
Data Science in Action
A Fortune 500 industrial equipment and services company had faced increased competition. With more than $15 billion in annual revenues, the company was a tour de force in its market.
But the management team wasn’t about to become complacent. Executives decided to better understand the brand position and craft a strategic goal that would align various business divisions.
The company engaged a third-party provider to survey 1,800 customers. Most of them were small to medium enterprises (SMEs), and the survey was created to collect feedback on several value drivers.
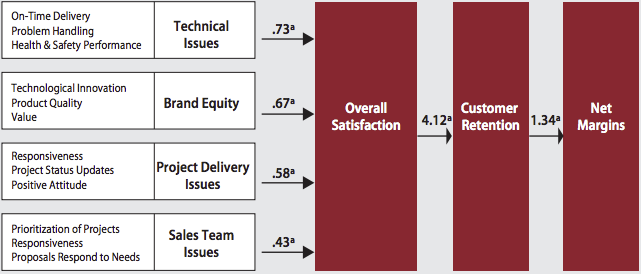
Customer-Based Execution and Strategy for the Industrial Equipment and Services Company, courtesy of C-CUBES™
The CUBES diagram shows that the top areas of customer experience relating to overall value were technical issues, brand equity, sales team issues
Management was surprised by the impact of technical issues on overall value. The executives had always assumed the main drivers for customer value were the company’s sales team and project delivery.
At the same time, the role of brand equity had a profound effect on their interpretation of branding. They realized it had genuine merit in a B2B context.
The analysis helped identify a subset of attributes that influenced customer perceptions within each strategic area.
For brand equity, they incorporated technological innovation, product quality
Equipped with this insight, the executives rallied all relevant business divisions around an improvement program; one that focused on brand equity and technical issues.
As a result, they could trace their efforts to a one-point gain in overall customer value. The company had increased retention by more than 4%, which equated to a marginal net gain of almost $200 million. An impressive achievement made possible by management’s decision to apply the CUBES framework.
Delivering a Strategic and Operational Roadmap
The Customer-Based Execution and Strategy framework empowers your leadership team to do several things. First, your executives can define what the strategic focus should be. Second, they can make informed investment decisions. And third, they can measure the outcomes of every initiative that’s undertaken.
Together, these capabilities form a compelling argument: the CUBES framework can shine a light on the path to greater profitability and help brands inspire belief.
But it takes a disciplined approach supported by carefully collected customer data, in-depth analysis and a clear set of strategic goals. Only then can you make meaningful changes, so your brand resonates with stakeholders and turns them into believers.
A Few Extra Insights
Hopefully, we've shed a bit of light on how to use data effectively to grow your brand and inspire belief. If you’re thinking through ways data science techniques can help you accelerate growth, we're happy to chat – or you can read this case study on how one company developed a renewed strategic focus through data science. Plus, here are a few more tips to help:
- Find out how you can use data analytics to optimize marketing spending.
- Learn about why brand research is so important when developing thoughtful brands.




